
What were the main findings from the trial and why are they significant?
MANDARA is the first head-to-head trial of biologics in patients with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) and the first to demonstrate that remission is an achievable treatment goal for EGPA patients with eosinophil-targeting biologic therapies. The MANDARA results also showed that treatment with Fasenra was associated with a greater reduction of blood eosinophil (a type of white blood cell) counts and more patients were able to taper off oral corticosteroids (OCS) versus the current biologic standard. Recognising the daily challenges faced by the patient communities living with inflammatory disorders like EGPA, pioneering research such as MANDARA aims to redefine patient care.
What is Fasenra (benralizumab) and why does it have potential for EGPA?
Fasenra is a monoclonal antibody that binds directly to the IL-5 receptor alpha on eosinophils, attracting natural killer cells to induce rapid and near-complete depletion of blood and tissue eosinophils in most patients via apoptosis (programmed cell death). There is a high unmet medical need in EGPA as there are limited treatment options and not all patients respond to currently available treatments.
First patients dosed with Fasenra in three dermatology trials
The comparator in the MANDARA trial is currently the only approved treatment for EGPA. Increasing the number of treatment options could help patients reduce chronic oral corticosteroid (OCS) usage and achieve remission, alleviating the burden of this disease.
What is the main reason eosinophil-targeting biologic therapies are promising treatments?
There is a high unmet medical need generally in inflammatory diseases and unfortunately, many patients remain unresponsive to those treatments that are currently available. Patients are typically treated with chronic high-dose OCS, but OCS can cause serious and lasting side-effects and patients often experience recurrent relapses when attempting to taper off these treatments.
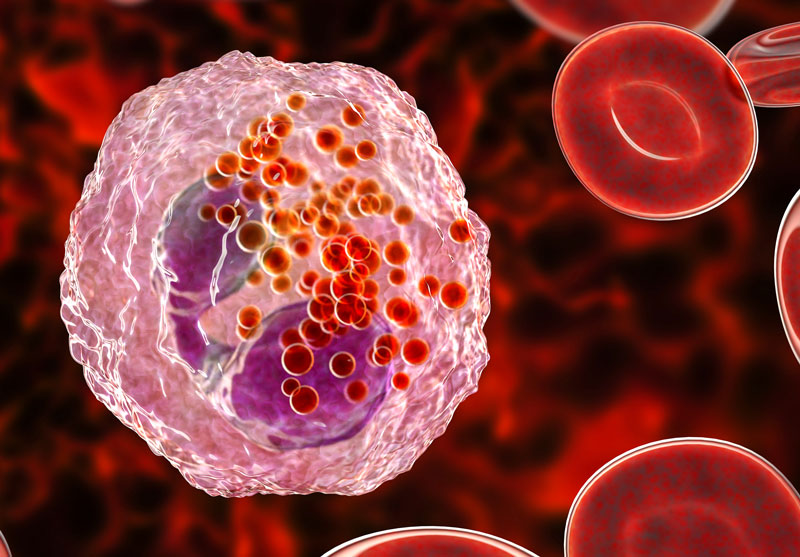
The MANDARA results showed that treatment with Fasenra was associated with a greater reduction of blood eosinophil counts
Studies on eosinophil-targeting biologics have demonstrated a consistently strong effect on near complete eosinophil depletion in blood and/or tissue.
What are the current main challenges in developing biologics?
While there are challenges in developing all new medicines, it is an exciting time with increasing numbers of patients eligible for treatment with a biologic globally. Treatment with benralizumab, an eosinophil-targeting biologic, leads to removal of eosinophils from blood and tissue, providing a targeted therapy for patients. Additionally, benralizumab has over ten years of clinical data demonstrating its safety and effectiveness for patients.
What does the future of monoclonal antibody therapies look like and how could this impact the pharmaceutical industry as a whole? What excites you most?
The future of monoclonal antibody therapies holds immense potential. Advanced technologies such as proteomics and artificial intelligence are also aiding in developing novel treatment combinations. One goal is to continue to develop precision medicines that deliver the right treatment to the right patient at the right time, offering hope for patients worldwide through ongoing innovation and research commitment.
About the interviewee
 Dr
Dr
The post Insights into
© Russell Publishing Limited, 2024. All Rights Reserved., source








